
We have covered e-invoices in some detail, and now it’s time to understand how taxation must be included in your invoices. Taxation can easily be added to invoices, provided the task/activity is taxable. The total tax payable must be prominently displayed on the invoice, and is contingent upon the tax laws of the country or jurisdiction in question. We will focus our attention on tax considerations for clients in the US, UK, EU, Australia and Canada.
What Are Some Tax Considerations When Creating Invoices?
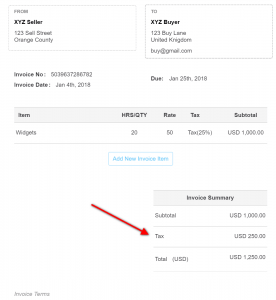

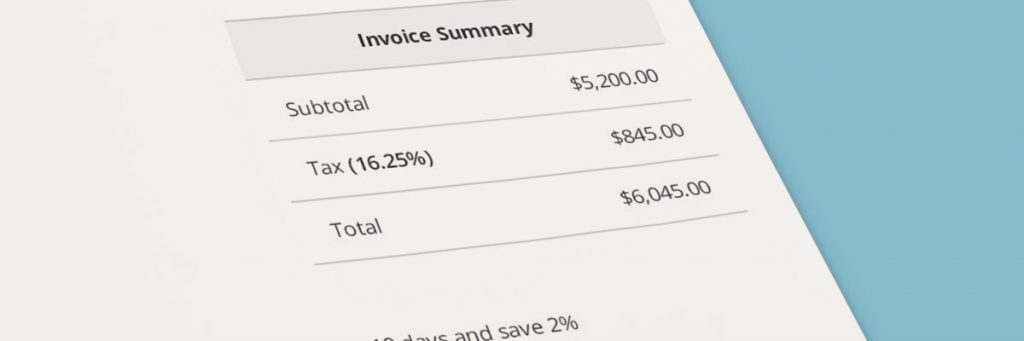
Once you are ready to create an invoice, it is important to comply with legal regulations in the country or jurisdiction you live in. These include tax-related considerations for your state or country. For starters, all invoices must prominently display the word ‘invoice’ on them. This is true for all e-invoices.
Unique numbers must be assigned to invoices to ensure that they are not confused with prior invoices or other invoices. Typically, invoices should include a breakdown of the price of goods or services provided before tax has been issued, the current tax rate, the total value of tax levied on the invoice, and the total amount payable at the bottom.
- Each country has different tax laws and requirements. For example, the United States recently passed sweeping legislation to overhaul the tax code and cap corporate taxes at 21%, and reducee personal income taxes across all tiers.
- Cross-border transactions are more common today than ever before, thanks to the Internet of Things, and globalization. Multinational corporations, and small businesses can have transactions originating in the US, with the transaction recipient in the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, or the EU, or any combination thereof.
- The introduction of e-invoices makes it possible for buyers and sellers to seamlessly transact with one another across international boundaries. This is when tax-related considerations become important. To effectively manage business operations, it is imperative that invoices are correctly filed, and the appropriate tax is applied.
Tax compliance is sacrosanct. The tax authorities in countries like the US, Canada, the UK and across the EU consider invoices as primary evidence of transactions. Further, they use these invoices to ascertain how much tax is owed by these multinational corporations and small businesses to the tax authorities.
In countries across Europe, including the UK, these taxes are known as VAT (Value Added Tax) or GST (General Sales Tax). Typically, VAT is paid monthly, or 4 times per year – quarterly. Believe it or not, VAT makes up 30% of government revenues.
VAT is applicable on multiple business operations, purchasing orders, and sales. Compliance with VAT and tax regulation is essential, and mandatory. Each country has unique requirements for VAT, and compliance with tax laws can be overwhelming for small business operations.
What Are the Challenges Associated with International Tax Considerations?
Global business is a complex phenomenon. Given that each country, territory, or jurisdiction has a specific set of tax rules and compliance procedures, it is imperative that invoices are accurate at all times. It can prove challenging to get trading partners to accept invoices if they do not meet with local requirements.
Here are several key points to remember when issuing taxes to clients (when buyers and sellers interact):
- Invoices must be kept for several years (check the law in your jurisdiction)
- All invoices must be tax compliant and validated
- The integrity and authenticity of invoices is inviolable
- All invoices must meet the minimum invoice content requirements
- Cross-border processing procedures and formality considerations must be considered
Why Is Tax Compliance on Invoices So Important?
Businesses are subject to auditing and risk being prosecuted by tax authorities if they do not comply with tax regulations. A company’s credibility may be undermined by its failure to comply with tax laws, and this may result in protracted audits or audits of trading partners. Fines for tax violations are very high. Not being tax compliant is simply a bad business practice.
Additionally, poor tax management will result in tax auditors interacting with other tax auditors from other countries to evaluate compliance-related issues in different jurisdictions. These are time-consuming proceedings, and will invariably rack up high costs for companies and business operations.
Tax compliance is important for several other reasons, notably:
- Incorrect or fraudulent invoices may be subject to tax/VAT collection
- Companies risk administrative fines and punitive measures for incorrect tax filings
- Companies that do not have correctly filed invoices may not be able to deduct tax or VAT
Taxation Around the World: A Guide to Compliant Invoicing
Given that each country has a unique tax code, it is imperative that invoices are correctly issued. Below you will find taxation data for various countries:
United States – The United States has a rather complex tax regimen, which differs from one state to the next. Certain states have no sales tax, or income tax, while others do. All US businesses are subject to federal taxation, which must be displayed on all invoices. Fortunately, electronic invoices automatically provide updated tax figures for US states, and apply them to the invoice. The state’s finance bureau provides information on the applicable tax for the invoice. Retail sales tax should typically be itemized on the invoice from US sellers.
United Kingdom – In the United Kingdom, any business that sells products/services must provide an invoice to the buyer and must be registered for VAT. Invoices act as acknowledgment of payments. All UK invoices must include certain pertinent information such as the date the customer must make payment, the amount that the customer needs to pay and various obligations that are applicable to the payment.
If the buyer and seller are VAT registered, then VAT invoices must be used. VAT invoices must be maintained in either paper or electronic format, and all copies must be kept safe even if they have been issued in error, or cancelled. In the UK, full VAT invoices must be used for retail supplies in excess of £250.
European Union – In the European Union, compliance with the EU VAT Directive is essential. The EU considers e-invoices the equivalent of paper invoices for legal purposes. Invoices are mandatory for VAT purposes for most business-to-business supplies and most business to consumer transactions.
Full VAT invoices must include pertinent information such as the date, a sequential invoice number, the supplier’s details, the customer’s details, the VAT rates applied, the VAT payable amount, a breakdown of VAT, any exemptions and the unit price of goods/services, rebates, discounts or exclusions. VAT rates vary across the EU, with countries like Austria at 20%, Belgium 21%, Croatia 25%, the Czech Republic 21% etc.
Australia – According to the Australian taxation office, tax invoices must meet the following requirements: personal details of the buyer and seller, the invoice date, the Australian business number, a description of the invoice, the GST amount (general sales tax), and the total price including GST. If the total invoice for sales issued by the seller to the buyer is 1,000 AUD +, then the buyer’s identity number or ABN must be displayed. Is important to note which items are taxable and which items are non-taxable.
Canada – There are several different provinces in Canada, and each of them has different tax rates. For example, SMBs in Alberta will have different tax requirements than businesses in Québec, Saskatchewan or Manitoba. In British Columbia for example, GST is 5% and PST is 7%. In Alberta, GST is 5%, and in Manitoba GST is 5%. In Ontario, HST is 13%, while in New Brunswick HST is 15%. These tax differences are important when it comes to invoicing clients correctly.
Now, you can appreciate the importance of tax considerations when issuing invoices to clients around the world. Buyers and sellers must be aware of this important component of business transactions, since the tax authorities are always watching.